1 Project Overview
lAIfe is an interactive simulation engine designed to explore causal relationships in narrative data. While traditional text-based games rely on pre-written decision trees, lAIfe utilizes Large Language Models (LLMs) to dynamically generate consequences based on user input and hidden state variables.
As the Team Lead and Lead Developer, I guided a four-person team to build this platform from concept to deployment. Our primary engineering challenge was orchestrating a seamless feedback loop between the user's frontend interaction and the backend's generative logic, ensuring the AI adhered to strict game rules while maintaining narrative creativity. This architecture secured us 1st Place in the AI Track at HackHayward 2025.
2 Technical Architecture
I designed a decoupled full-stack architecture to ensure scalability and maintainability:
2.1 Frontend: React + TypeScript + Vite
- Type Safety: Migrated the codebase to TypeScript to enforce strict typing on game states (e.g., character stats, inventory), significantly reducing runtime errors during complex simulation branches.
- Performance: Utilized Vite for optimized building and HMR (Hot Module Replacement), ensuring a smooth developer experience and fast production load times.
- Responsive UI: Implemented a component-based UI that renders dynamic narrative blocks and interactive decision nodes, adapting in real-time to the AI's output.
2.2 Backend: Python (Flask) & AI Orchestration
- API Design: Developed a RESTful API using Flask to handle game logic, session initialization, and prompt construction.
- Low-Latency Inference: Integrated Groq API for LLM processing. By leveraging Groq's LPU (Language Processing Unit) architecture, we achieved near-instantaneous token generation, which is critical for maintaining immersion in a turn-based simulation.
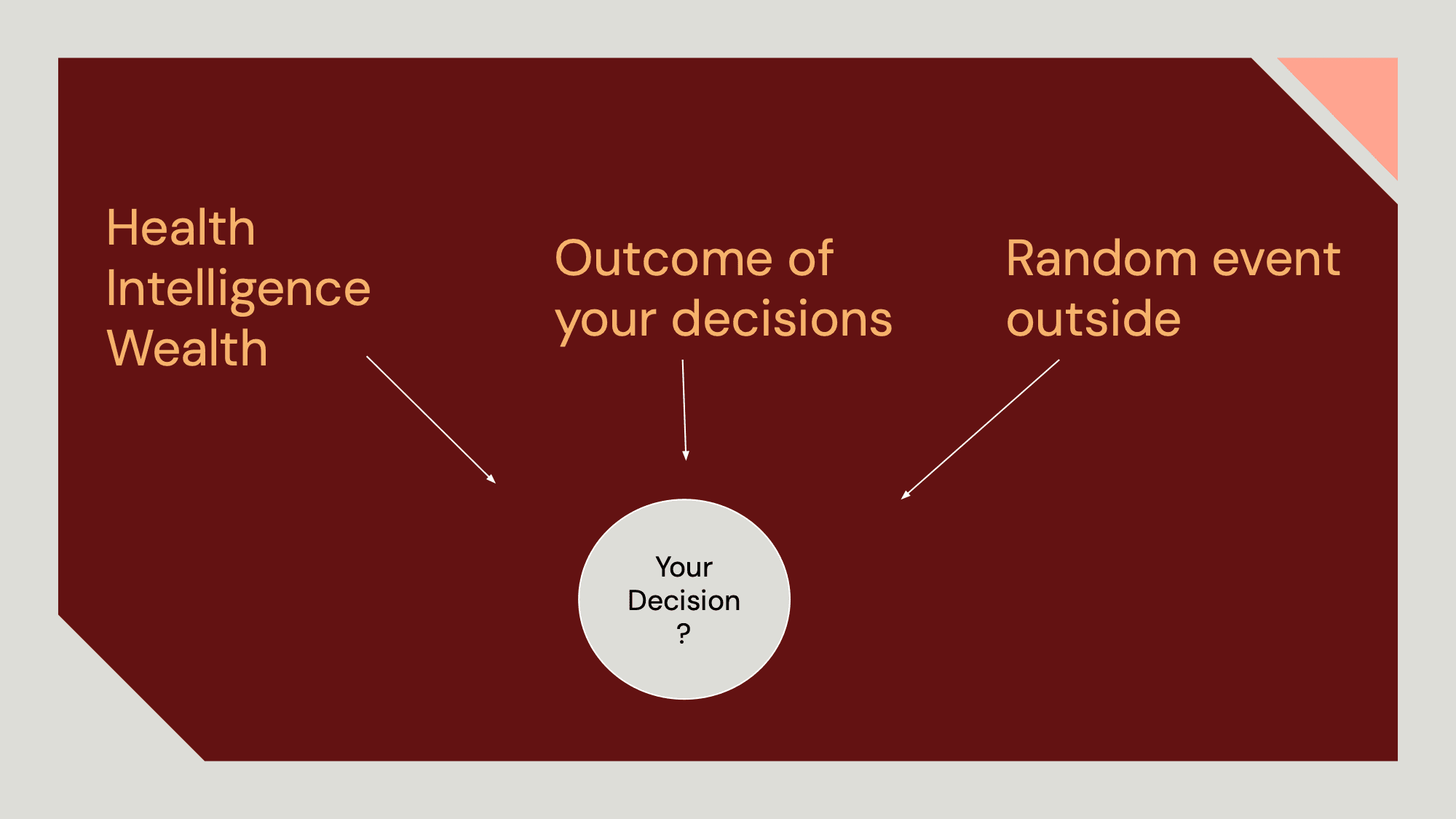
- State Management System: I engineered a robust JSON-based state manager that persists simulation context across turns. This system tracks user choices, character attributes (Health, Wealth, Intelligence), and narrative history, injecting them into the LLM context window at each turn to prevent hallucinations and ensure continuity.
3 Key Feature: "Night City" Logic Engine
To stress-test our architecture, we developed the "Night City Version," a cyberpunk simulation module requiring complex rule enforcement.
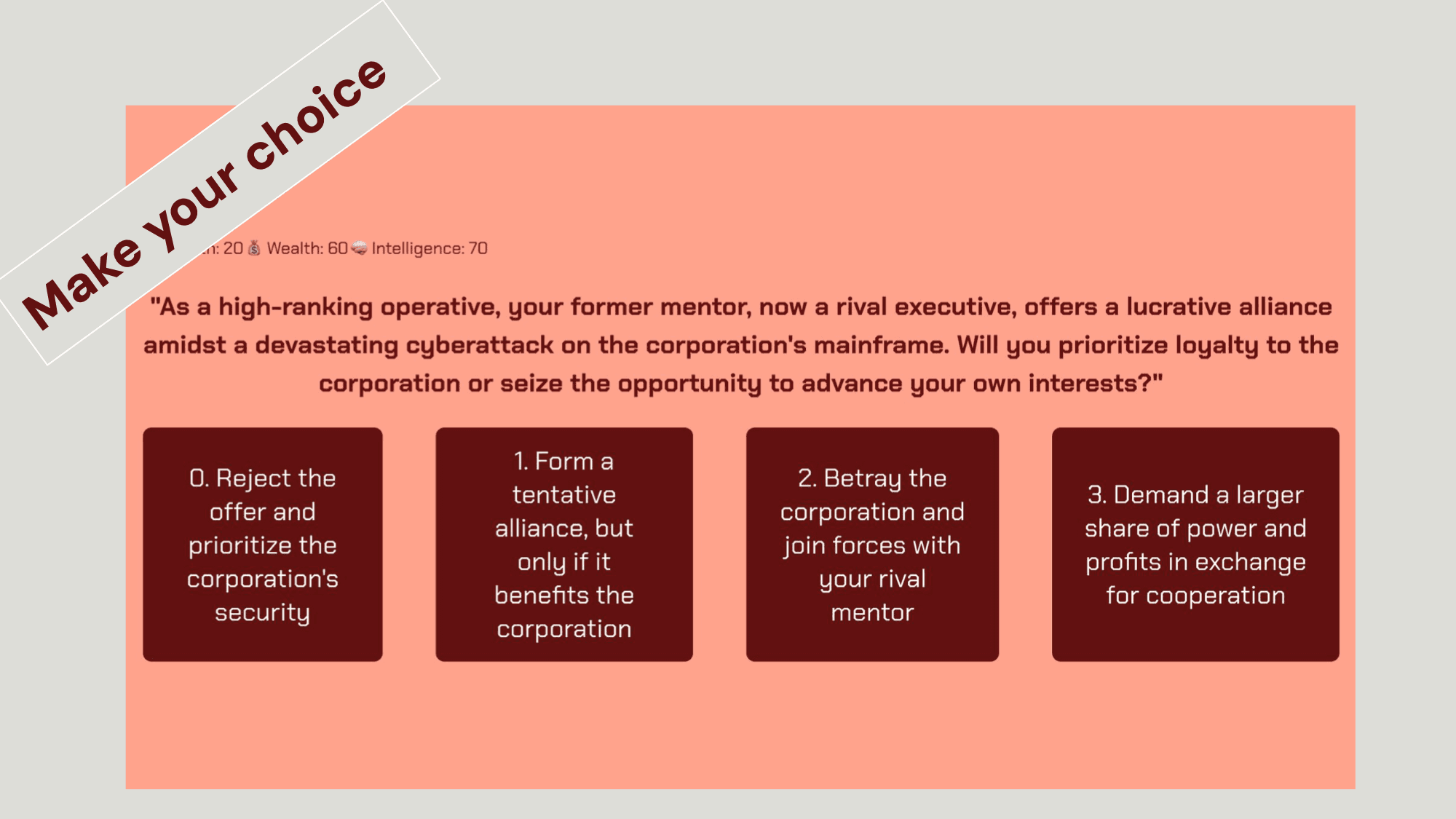
- Dynamic Attribute Tracking: Unlike standard chatbots, this module tracks three distinct variables: Health, Intelligence, and Wealth. I implemented backend logic to parse the LLM's raw text output, extract numerical changes, and update the user's state JSON automatically.
- Structured Prompt Engineering: Designed a "System Prompt" framework that forces the LLM to act as a Game Master, outputting structured data alongside narrative text. This ensured the game logic (e.g., "If Wealth < 0, trigger Game Over") executed reliably across 10 distinct simulation rounds.
4 Future Engineering
The project is currently evolving from a hackathon prototype into a robust educational tool. I am currently working on:
- Long-form Context: Implementing RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) to support "Full Life Cycle" simulations (Birth to Old Age) without exceeding token limits.
- Analytics Integration: Building a pipeline to aggregate user decision data for behavioral research applications.
5 Selected Visuals